CIMD Clients
Support URL-based client IDs for MCP tools and dynamic clients using RFC 9728
oauth2 cimd client id metadata document rfc 9728 mcp url-based dynamicClient ID Metadata Document (CIMD) clients use a URL as their client ID instead of a pre-registered identifier. This follows draft-ietf-oauth-client-id-metadata-document-00 and is designed for tools that need to dynamically register with authorization servers — most notably MCP (Model Context Protocol) servers.
When to Use
Section titled “When to Use”CIMD is for scenarios where:
- The third-party app cannot pre-register a client (e.g. an MCP tool connecting to many different auth providers)
- You want to support dynamic clients without manual registration
- The tool follows RFC 9728 for client metadata discovery
Enabling CIMD
Section titled “Enabling CIMD”CIMD must be explicitly enabled. Go to your project’s dashboard, then Settings → OAuth2 Provider and toggle Client ID Metadata Document, or add it to your nhost.toml:
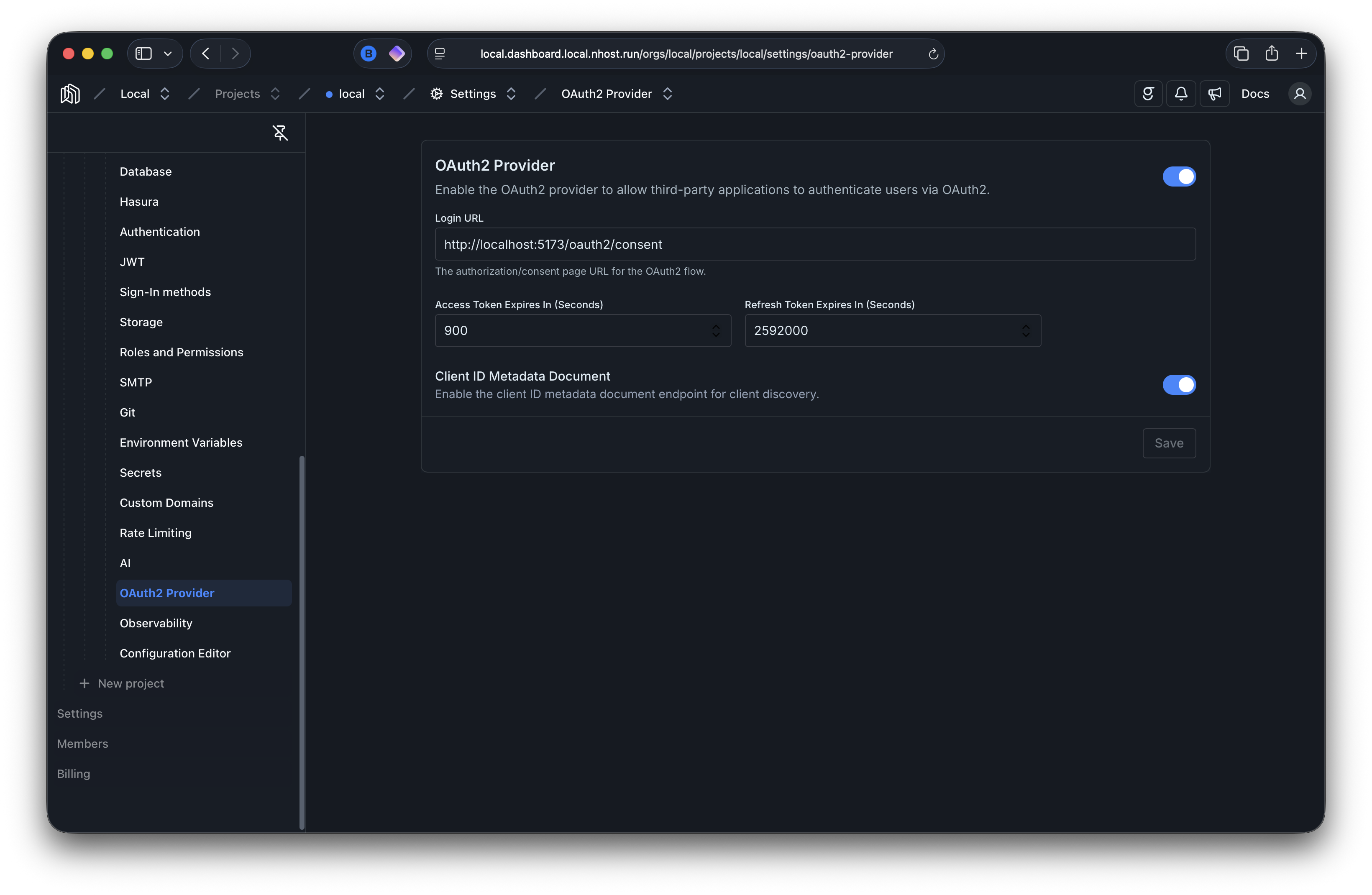
[auth.oauth2Provider]# Enable the OAuth2/OIDC providerenabled = true # default: false
[auth.oauth2Provider.clientIdMetadataDocument]# Enable Client ID Metadata Document (CIMD) supportenabled = true # default: falseHow It Works
Section titled “How It Works”Instead of a pre-registered nhoa_... client ID, the third-party app provides an HTTPS URL as its client_id in the authorization request. Nhost Auth:
- Fetches the metadata document from that URL
- Validates the metadata (redirect URIs, scopes, grant types)
- Creates or updates the client record automatically
- Proceeds with the standard authorization code flow
The metadata document hosted at the client ID URL looks like:
{ "client_id": "https://my-mcp-tool.example.com/oauth/client.json", "redirect_uris": ["https://my-mcp-tool.example.com/callback"], "scope": "openid profile email", "grant_types": ["authorization_code"], "response_types": ["code"], "token_endpoint_auth_method": "none"}CIMD clients are always public (no secret) and must use PKCE.
Security
Section titled “Security”Nhost Auth enforces several security measures when fetching client metadata:
- The
client_idURL must use HTTPS (HTTP is only allowed in development) - The URL must have a non-trivial path, no fragment, no credentials, and no dot segments
- Private and loopback IP addresses are blocked (SSRF protection)
- DNS rebinding protection is enforced
- Metadata is cached for 1 hour to avoid excessive fetching
- Maximum response size is 5 KB with a 5-second timeout
- Redirect URIs in the metadata must be on the same origin as the client ID URL